Author: Moritz Shore
Date: October, 2025
Introduction
SeNorge2018 is a gridded (daily, 1x1km) dataset for Norway with temperature and precipitation stretching from 1957 to present day.
Here are some useful links:
miljotools helps you access this dataset by allowing you
to download and apply a subset of the data that interests you. You can
do this by:
- Determining your coordinate window
- Building your download query
- Downloading your queries
- Extracting data in “.csv” format.
- Apply data to models
Workflow
We need to provide a shapefile (polygon) of our desired area to download. In this example we will download the following publicly available watershed file:
download.file(url = "https://gitlab.nibio.no/moritzshore/example-files/-/raw/main/MetNoReanalysisV3/cs10_basin.zip", destfile = "cs10_basin.zip")
unzip("cs10_basin.zip")
cs10_basin = "cs10_basin/cs10_basin.shp"
example_polygon_geometry <- read_sf(cs10_basin)
map1 <- mapview(example_polygon_geometry, alpha.regions = .3, legend = F)
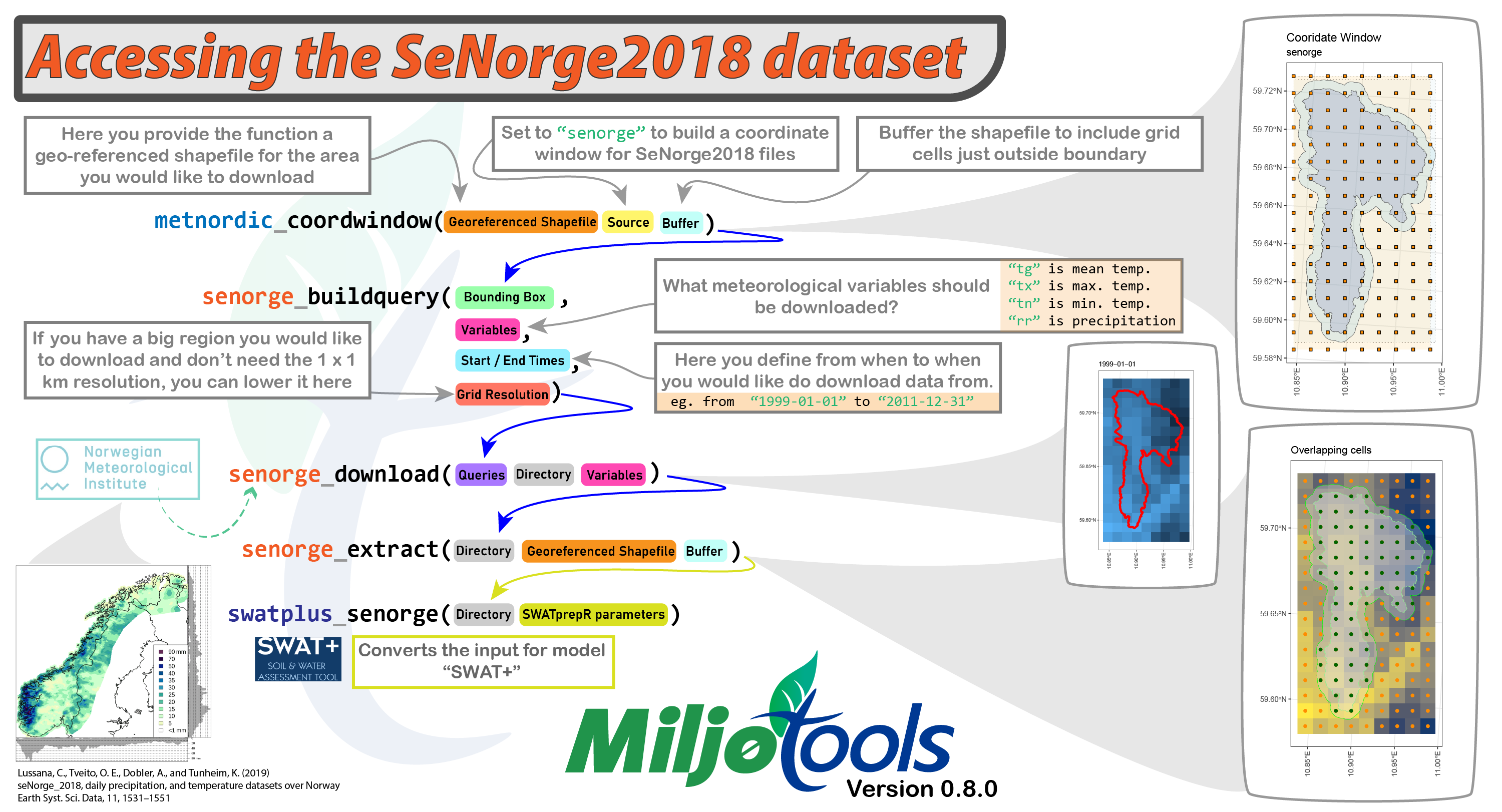
map1We can use the same function as for the MET Nordic dataset for SeNorge, we just need to adjust the “project” parameter. We will also buffer the shapefile by 500 m to include grid cells just outside the boundaries.
my_coord_window <- metnordic_coordwindow(
area_path = example_polygon_geometry,
area_buffer = 500,
source = "senorge",
verbose = TRUE,
interactive = FALSE
)## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> getting base file from: SeNorge2018
## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> basefile downloaded.
## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> Loading and projecting shapefile...
## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> geometry detected: sfc_POLYGON
## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> buffering shapefile: 500 m
## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> calculating coordinate window...
## miljo🌿tools > metnordic_coordwindow >> coordinate window is: xmin=341 xmax=349 xmin=1388 ymax=1372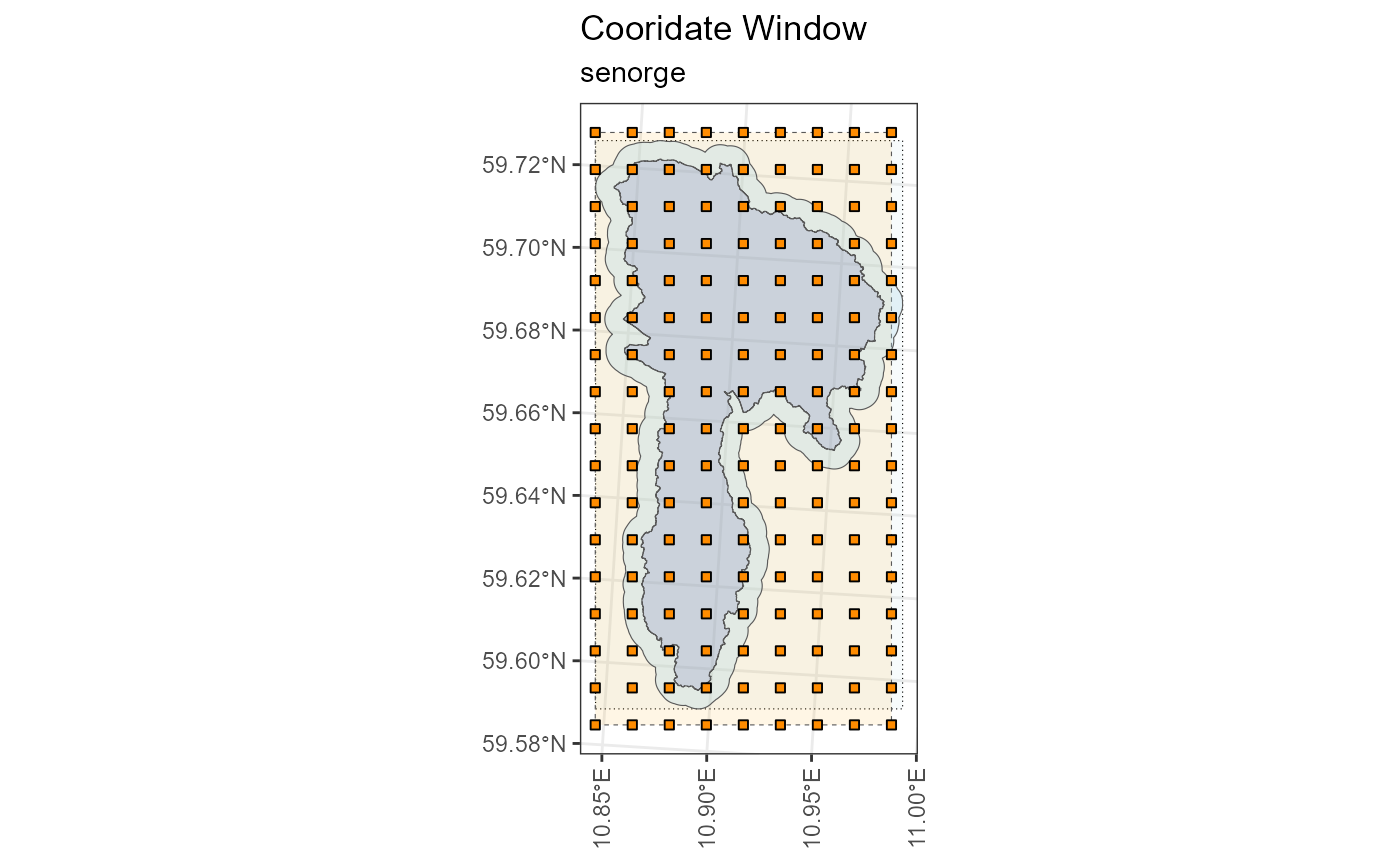
Now we can use this coordinate window to build our download queries.
At this stage we need to define which variables we should like to
download, at which resolution, and for which time period. In this
example we are downloading all the variables (tg = mean
daily temperature, tn = minimum daily temperature,
tx = maximum daily temperature, rr = total
daily precipitation), from a random day in 1999 to a random day in 2001.
We are doing this at a grid resolution of 1x1.
my_queries <- senorge_buildquery(
bounding_coords = my_coord_window,
variables = c("tg", "tn", "tx", "rr"),
fromdate = "1999-12-30",
todate = "2000-01-02",
grid_resolution = 1,
verbose = TRUE
)## miljo🌿tools > senorge_buildquery >> You have a grid of: 8 x 16 (128 cells)
## miljo🌿tools > senorge_buildquery >> generating urls with a grid resolution of: 1 x 1 km
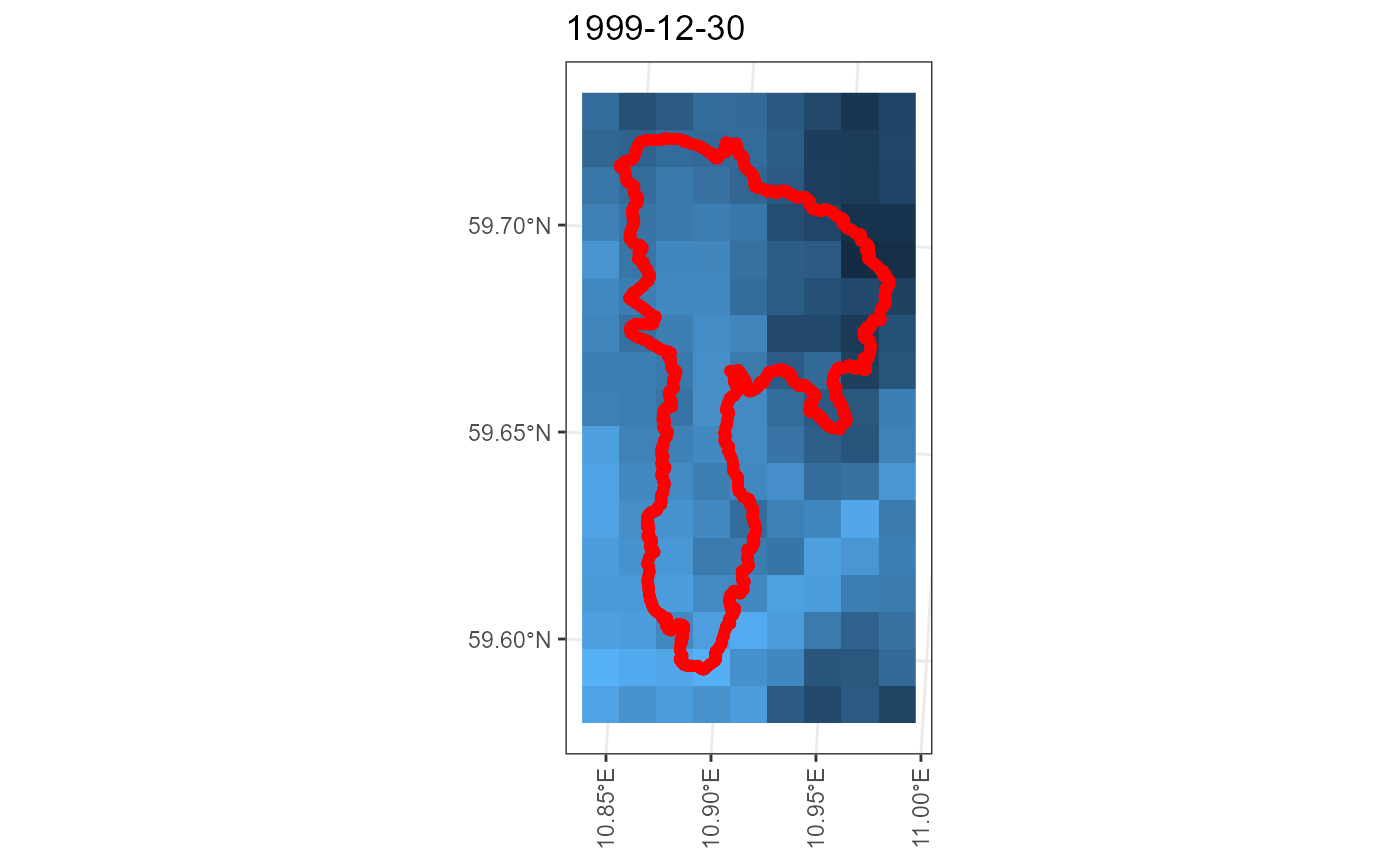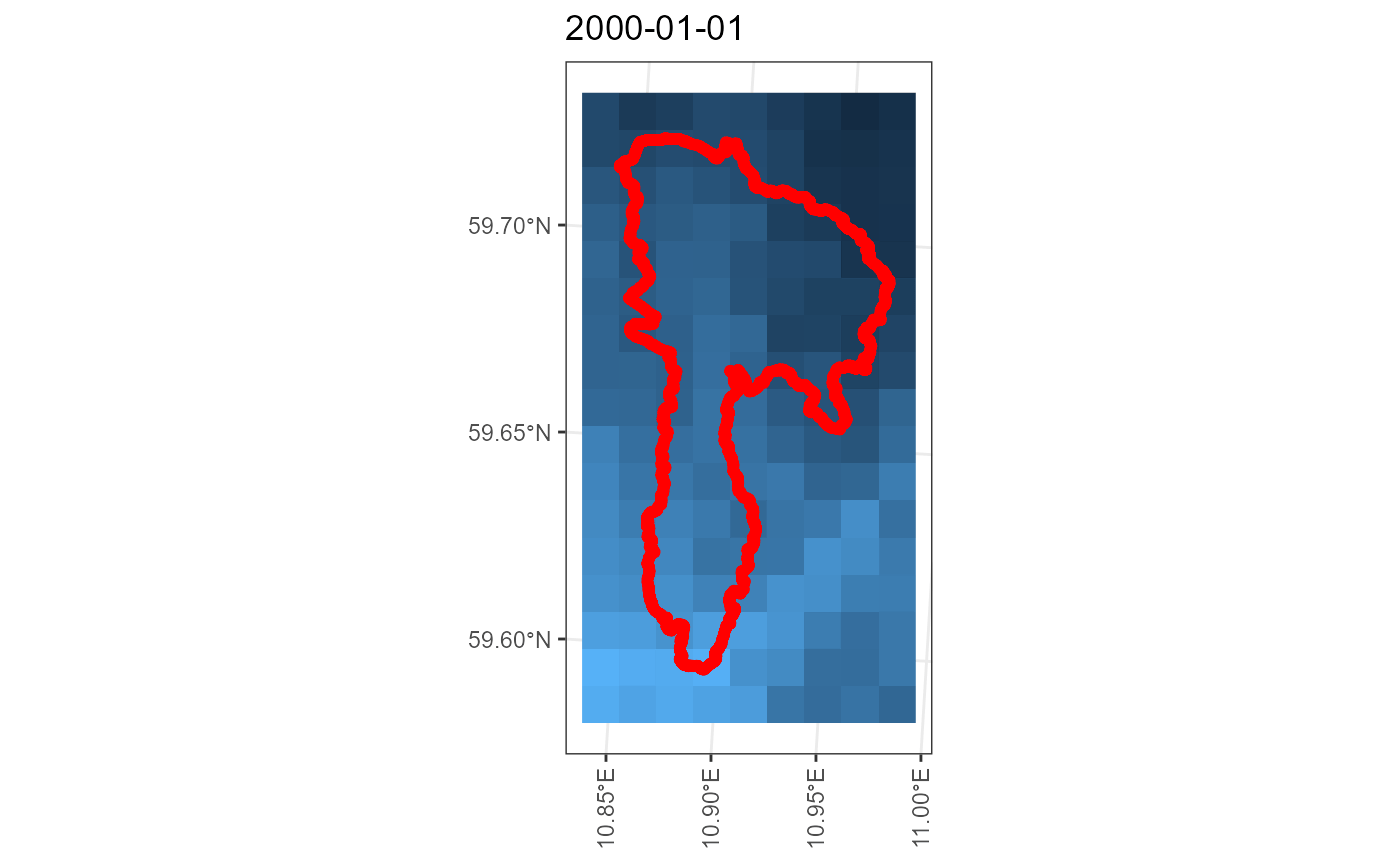
## miljo🌿tools > senorge_buildquery >> Returning queries.. (2)Now that we have our queries, we can download our customized files. We can provide our polygon to double check that the download matches the area we want.
my_download <- senorge_download(
queries = my_queries,
directory = "senorge_download",
variables = c("tg", "tn", "tx", "rr"),
polygon = example_polygon_geometry,
verbose = FALSE
)
Diagnostic plots
With our files downloaded in .nc format, we can convert
them to .csv for the grid cells that cover our desired
area. (Note: at this stage you can use a different, smaller polgyon if
you only want to extract a smaller subset of the available data)
senorge_extract_grid(
directory = my_download,
outdir = "senorge_extract_grid",
area = example_polygon_geometry,
variables = c("tg", "tn", "tx", "rr"),
buffer = 500,
verbose = FALSE,
map = TRUE
) -> my_extract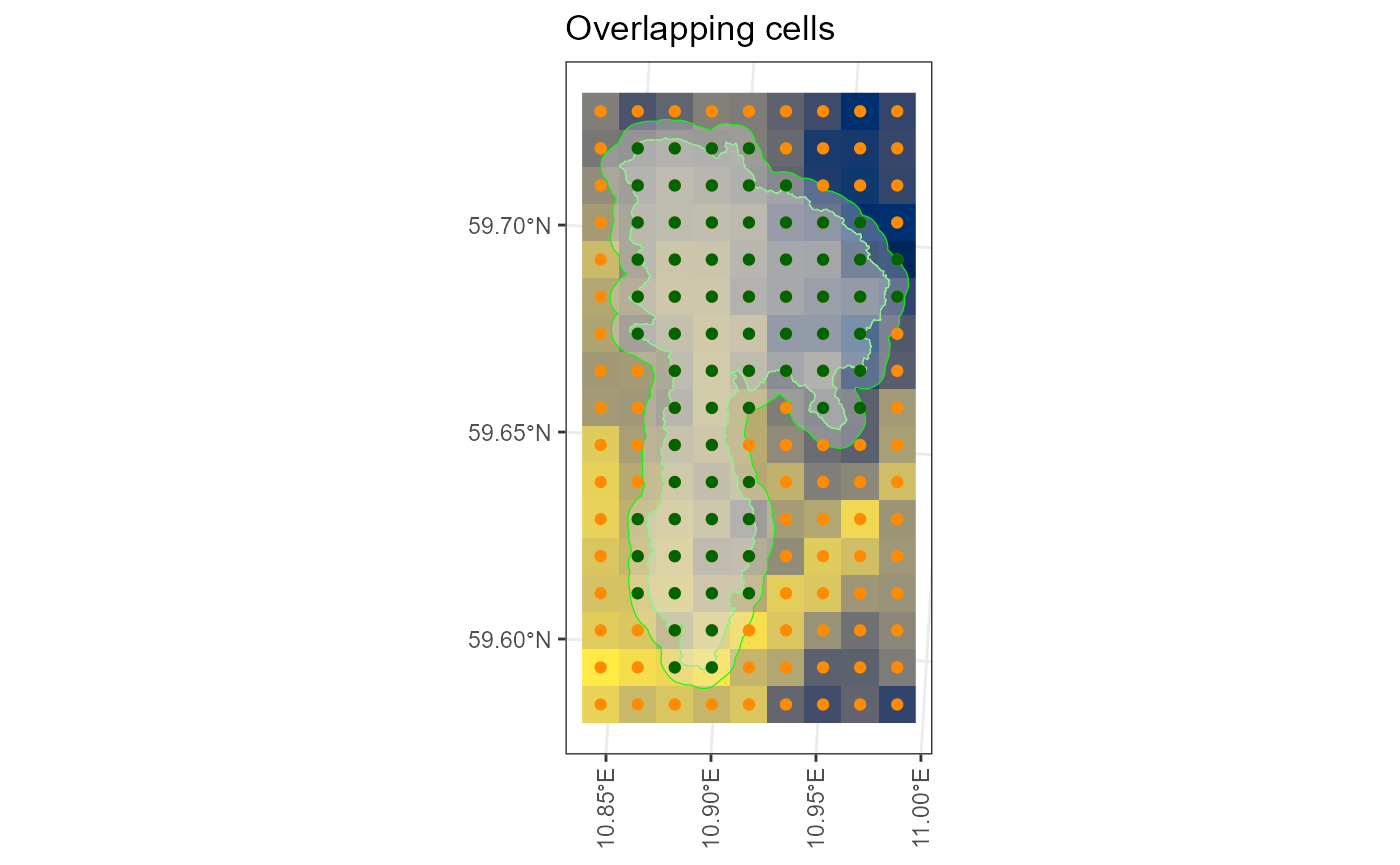
Having a look at the results:
list.files(my_extract, pattern = ".csv", full.names = T)[1] %>% readr::read_csv(show_col_types = FALSE)## # A tibble: 4 × 6
## vstation date tg tn tx rr
## <dbl> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1 1999-12-30 -5.59 -10.7 -4.42 0
## 2 1 1999-12-31 -9.61 -13.5 -8.46 0
## 3 1 2000-01-01 -9.35 -9.35 -2.75 10.3
## 4 1 2000-01-02 -5.45 -6.39 3.16 0.47
metadata_path = list.files(my_extract, pattern = ".shp", full.names = T)
metadata_path %>% sf::read_sf() %>% mapview::mapview(label = "vstation", legend = FALSE)Model Connections
If you are using SWAT+ you can apply the SeNorge data to your setup using the following function:
swatplus_senorge(
extract_path = my_extract,
metadata = metadata_path,
DEM = "../../swat-cs10/model_data/input/elevation/cs10_dem_1m_utm33n.tif",
aux_data = "../../swat-cs10/model_data/input/met/cs10_weather_data.xlsx",
epsg_code = 25832,
write_path = "../../mt-testing/MetNord_MN2/",
verbose = FALSE
)